Electric vehicles (EVs) and plug-in hybrids are becoming more and more popular, but the infrastructure for EV chargers is still being built. If you’re thinking of getting an EV or you recently made the upgrade, it’s important to know where to charge your car, how much it costs, which plugs and adapters you need to use, and more. In this guide, we will go over everything you need to know about charging your EV at home and on the road, so you’ll be prepared.
The Benefits of EV Charging
The growth of electric vehicles comes with a lot of benefits. It will help the environment by lowering carbon emissions. With rising gas prices, charging an electric car is now much cheaper than filling up at the pump. Plus, with an EV charger in your home, you’ll never have to worry about your batteries dying again.
Level 1, Level 2, and Level 3 EV Chargers
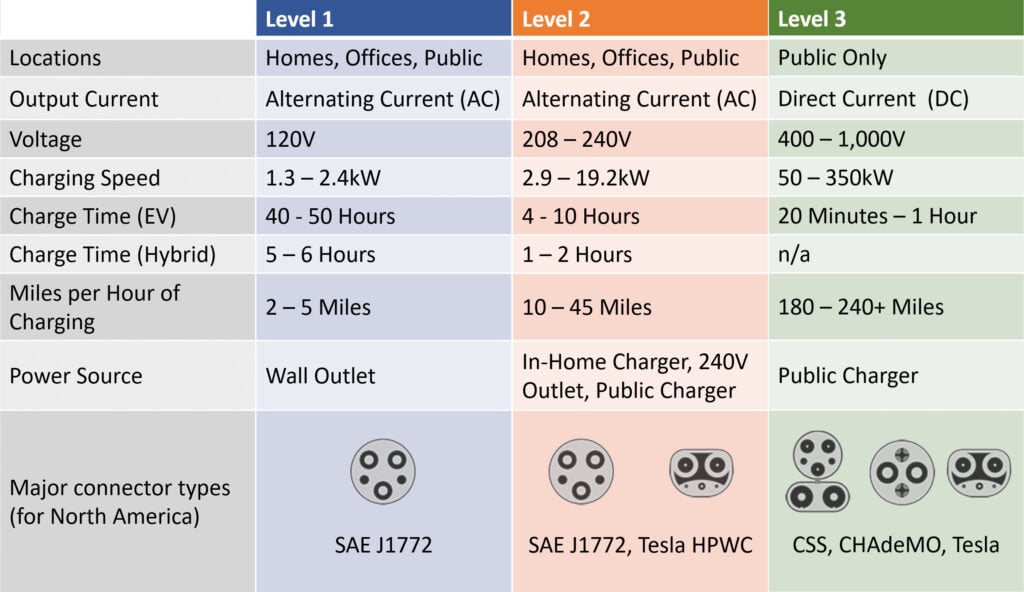
There are three levels of EV charging, each of which delivers different amounts of power. Level 1 chargers are too slow for most owners, but level 2 chargers can fill up your batteries overnight, making them perfect for installing at home. Level 3 chargers are the fastest, but they are only found in public charging stations.
Read More: Level 1 vs level 2 EV charging
Level 1 EV Charger Guide
Level 1 chargers are just regular electrical outlets that you can find on the walls. These plugs carry 120V (Volts), making them the slowest way to charge your electric car. You won’t need to install anything extra, but you will need a special cable to connect your EV to a wall outlet.
Many electric vehicles will come with a level 1 charging cable for free, or you can always buy one for around $200. Even if you don’t plan on using a level 1 charger every night, it’s a good idea to keep one in the car in case of emergencies.

Although level 1 chargers are the cheapest and easiest solutions, they only give you enough power to drive up to 30-40 miles a day. Studies also show that EV batteries charge 36% slower when it’s 32 degrees compared to 77 degrees. So, you might want to upgrade to a level 2 charger if you live in a cold area.
Level 2 EV Charger Guide
Level 2 chargers carry up to 240V, which means they can fill up your batteries around eight times faster than a level 1 charger. You can typically find level 2 chargers in offices and public charging stations, but you can also install a level 2 charger in your home to keep your EV charged overnight.
Most states require an electrical permit and inspections to install a level 2 charger in your home, and you might need to hire a certified electrician to install it for you. There are two different types of EV chargers you can install in your home: a hardwired charging station or a special 240V outlet.
Read More: How to choose the right EV charger

You should consider installing a level 2 charger in your home if you drive your electric car daily and you want to save money on gas. If you want to save even more money, installing solar panels on your roof can cut your energy costs and possibly keep your EV charged for free.
Level 3 EV Charger Guide
Level 3 chargers are usually only found in public places, like Tesla Superchargers or other charging stations. Unlike level 1 and 2 chargers, which use AC (alternating current), level 3 chargers use DC (direct current). This allows them to charge your electric vehicle in as little as 20 minutes.
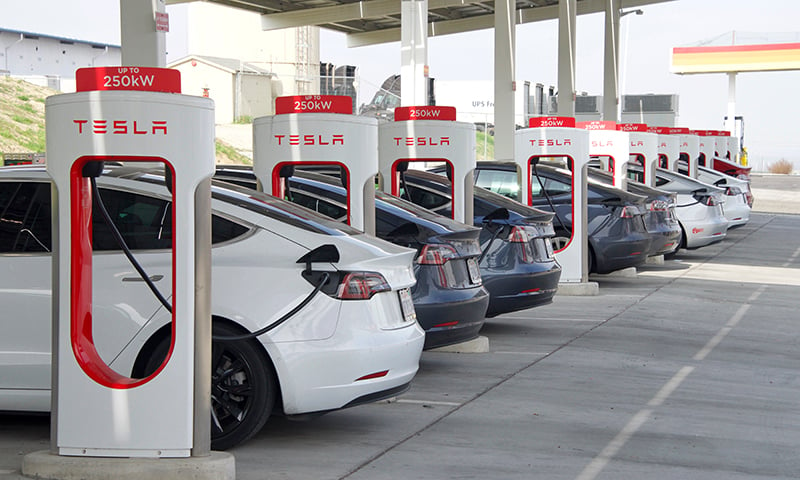

Direct current is much more dangerous than alternating current, and it requires a certain infrastructure. So, it’s not realistic for most people to install a level 3 EV charging station in their homes.
How Long Does It Take to Charge an EV?
It can take up to several days to fully charge an EV with a level 1 charger, while it will only take around 10 hours with a level 2 charger. With a level 3 charger, you can fill up your electric car in less than an hour, according to data from the US Department of Transportation.
However, there are many other factors that go into how long it takes to charge your electric vehicle, including the size of your battery, the temperature, the state of your battery, how much charge it already has, the current electrical demand in your area, and more.
It’s important to note that electric vehicles usually reduce charging speed or stop charging altogether at around 80% in order to increase the life of your batteries. While you can charge your car to 100%, it’s usually not advised unless you are taking a long trip.
Many electric vehicles will come with a companion smartphone app, which usually lets you see how fast your car is charging, create charging schedules to save electricity, and more.
Read More: How long does it take to charge an electric car?
Types of EV Connectors
Currently, most electric cars use SAE J1772 connectors for level 1 and level 2 chargers. For level 3 chargers, most EVs use a CSS connector. The major exception is Tesla, which uses NACS connectors and adapters. Some Japanese manufacturers also use the CHAdeMO plug for EVs in the US.
However, it’s important to note that most automakers will switch to Tesla’s NACS ports for all electric cars made for US markets starting in 2025.
SAE J1772
The SAE J1772 plug is currently the standard connector used for almost all level 1 and level 2 chargers in North America, unless you have a Tesla. Also known as a “J plug” or “Type 1,” you can identify the SAE J1772 by its five pins arranged in a circle. This connector is rated for everything from 1.4 kW to 19.2 kW.
If you have a Tesla, it will use a different connector, but you can still use most level 1 or level 2 chargers with a NACS to SAE J1772 adapter. Thankfully, Tesla includes this adapter when you buy a new car, but you can also purchase it separately.

If your electric vehicle has an SAE J1772 port, you can use a CSS connector or an adapter for level 3 fast chargers.
CCS Connector
The CCS (Combined Charging System) plug is currently the standard connector for level 3 chargers in the US, except for Tesla. These plugs combine the same 5-pin array from the J1772 at the top with an additional two pins on the bottom that provide DC fast charging speeds up to 350kW.

As of 2024, almost all newly manufactured electric vehicles made for the US will have a CCS charging port, but many automakers will make the switch to NACS by 2025.
Tesla (NACS) Connector
Since Tesla was one of the first electric vehicle manufacturers, they designed their own EV charging plug. The NACS (North American Charging Standard) can be used for both AC and DC charging and provides up to 250kW of power. However, you will need to use adapters when connecting to non-Tesla EV chargers.
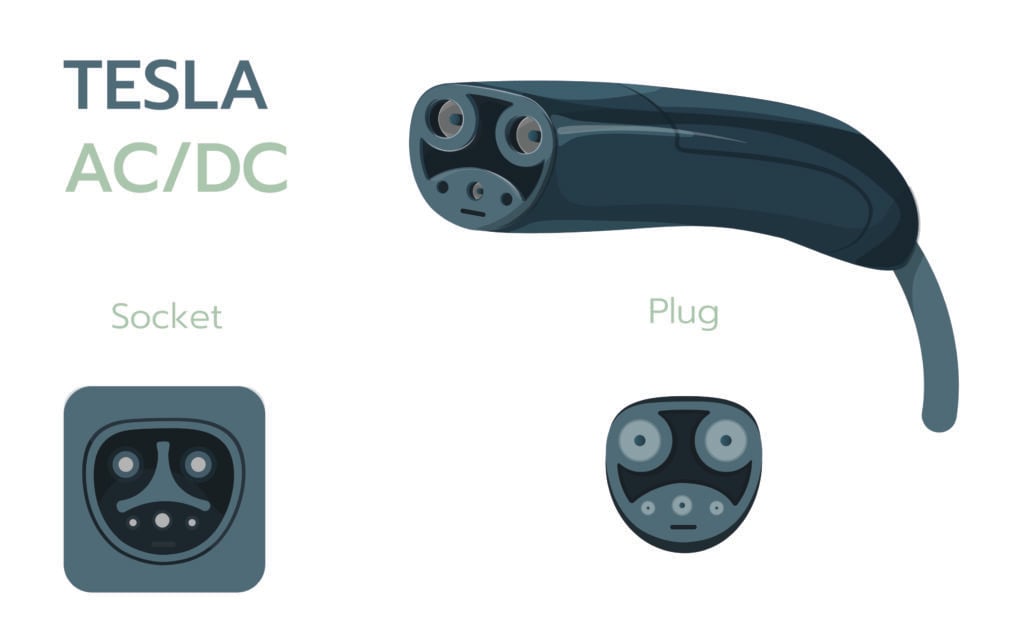

In 2022, Tesla opened the design for NACS to the public, and now other automakers are allowed to add the charging port to their electric vehicles. Since Tesla already owns 60% of DC fast charging EV stations in the US, many automakers have agreed to add the NACS charging port to all new electric cars starting in 2025, including:
- GM (which owns Chevrolet, Cadillac, and Buick)
- BMW (which owns Mini and Rolls-Royce)
- Volkswagen (which owns Audi and Porsche)
- Honda
- Nissan
- Ford
- Subaru
- Kia
- Volvo
- Mercedes-Benz
- Hyundai
- Jaguar
Toyota (which owns Lexus) says it will also be switching to NACS for “certain” hybrid models by 2025. Plus, current Toyota and Lexus EV owners will “be offered access to an adapter to enable NACS charging starting in 2025.”
Many other manufacturers will also provide existing EV owners with plug adapters and software updates to make their cars compatible with Tesla Superchargers before the switch occurs in 2025.
CHAdeMO
There are a variety of other connectors available to charge EVs, but they are most common in other countries. If you buy an EV from a Japanese automaker, like the Nissan LEAF, there’s a chance it will use the CHAdeMO connector. Short for “Charge de Move,” this plug typically supplies 62kW to 150 kW of power.
A new edition of the CHAdeMO protocol has been developed that supplies up to 500kW of power. However, most automakers that are still using CHAdeMO in the US will be switching to NACS connectors by 2025.
EV Charging Adapter Guide
In order to charge an EV, there’s a chance you’ll need to use an adapter. These small devices usually fit right on top of the plug and snap into place. Then, you can charge your Tesla with a CCS plug or vice versa. With the right adapters, you can use almost any charging station for your electric car.

It’s also important to know there are several different types of electrical outlets you can use for level 2 chargers. So, make sure to check exactly which 240V NEMA outlet you have before installing a level 2 charger.
How Much Does It Cost To Charge an Electric Vehicle?
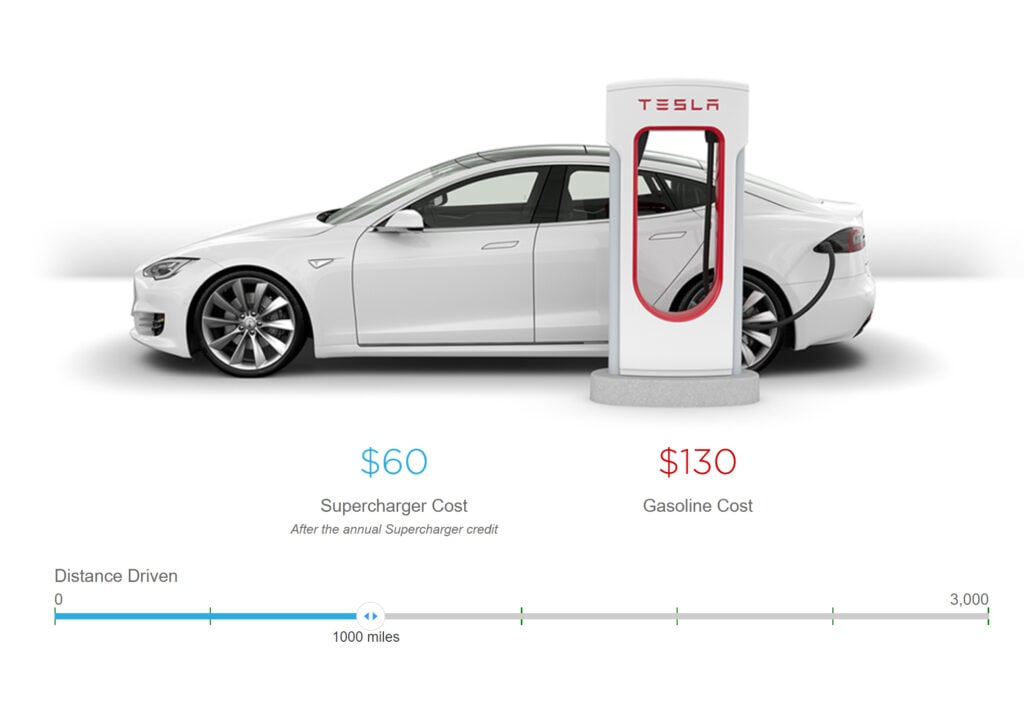
Charging an electric vehicle costs the average American nearly $60 a month, according to the Department of Energy, assuming you drive around 1,000 miles and your EV gets 3 miles per kWh. To compare, the average American now spends $150-$200 a month at the gas pump, according to JD Power.
Electricity prices can change dramatically depending on demand in your area and infrastructure issues that occur, especially during weather events. To save money, you should avoid charging your electric vehicle during peak hours, so it’s best to plug your car in overnight, when demand is at its lowest.
To find how much it will cost to charge your electric car, use this calculator from the Department of Energy. You can compare the cost of vehicles made since 2009 in terms of the annual fuel/electricity costs, the cost per mile, and other data based on the state where you live and your average driving habits.
Read More: How long does it take to charge an electric car?
How To Find an EV Charger Near You
There are over 60,000 public EV charging stations across the country, with the majority of them in California. To find a charging station near you, this map from the Department of Energy will show you how many connectors are available at each station.
You can also use smartphone apps to guide you to public EV charging stations near you, including PlugShare, Electrify America, ChargeHub, ChargePoint, EVgo, and more. Most will show you different kinds of information about charging stations, while only a few will let you charge your car remotely.
How To Install an EV Charger at Home
To install a level 2 EV charger in your home, you first need to decide whether you want it hardwired or if you want to install a 240V outlet. If you already have a high-powered outlet in your garage, you might just be able to plug an EV charger in and mount it on the wall. Otherwise, you’ll need a professional to install it for you.
Even if you already have a 240V outlet, you still might need to upgrade your home’s electrical system. If your home only has a 100-amp panel, you might need to upgrade to a 200-amp panel in order to handle your new EV charger on top of other major electrical appliances in your home.
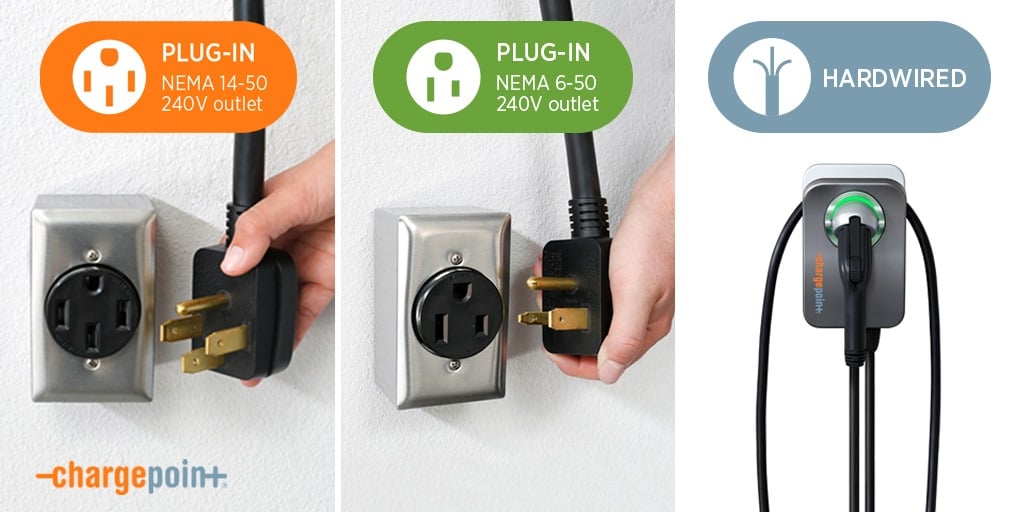

A hardwired EV charger connects directly to a dedicated circuit in your electrical panel. This will require a licensed electrician to rewire your electrical system, upgrade your circuit breaker, and maybe even shut down the power to your entire home.
Hardwiring your EV charger makes it more secure and reliable, but installing a 240V plug makes it easier to swap out your EV charger if it fails or when a better model comes out in the future.
If your home was constructed after 1970, there’s a good chance that you can install an EV charger without any modifications or upgrades. Most states will also require you to have a permit to install an EV charger in your home.
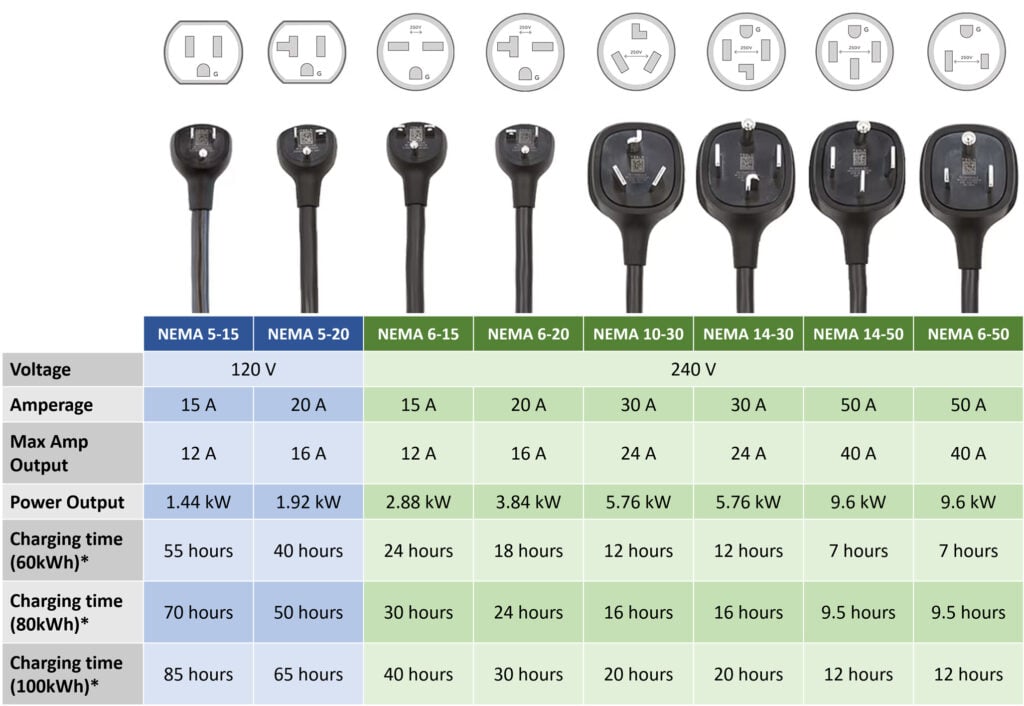
Types of NEMA Plugs
If your home has a 3- or 4-prong outlet, it might support an EV charge, but different NEMA outlets have different power ratings. NEMA 6-50 and NEMA 14-50 are some of the most common plugs that support level 2 charging, while NEMA 5-15 and other plugs only support level 1 charging.
How Much Does It Cost to Install an EV Charger at Home?
A level 2 charger will cost you anywhere from $200-$1,000 and up, just for the hardware itself. Then, you’ll need to pay for the installation, which varies based on your electrical system, how far your circuit breaker is, and more. Overall, the average American spends $1,000-$2,500 installing an EV charger in their home.
Read More: The best EV chargers to install in your home
If you need any help installing your EV charger, HelloTech can send an electrician to your door to give you a free quote. We can provide an in-home quote in as little as 15-30 minutes, and our technicians can schedule your installation within a week or two of the estimate.






