If you’ve been exploring EV chargers, you probably noticed some models showcasing how many amps they can deliver. This electrical metric lets you know a charger’s power draw and charging speed. Here’s a comprehensive guide on how many amps your EV charger needs, evaluating your home’s power capacity, and more.
What Are Amps?
Amps are a measurement of the electrical current in a circuit. Basically, the more amps a circuit has, the more electrons are flowing through it. Volts measure the pressure of electrons in a circuit. With both of these metrics, you’ll know how many watts it can deliver, or the overall power output.
To make things simple, think of the electricity flowing to your EV like water traveling through a hose. In this analogy, amps would be like the sizeof the hose, while volts would be like the pressure of the water. To deliver as much power to your EV as possible, you’ll want an EV charger with a high voltage and amperage.

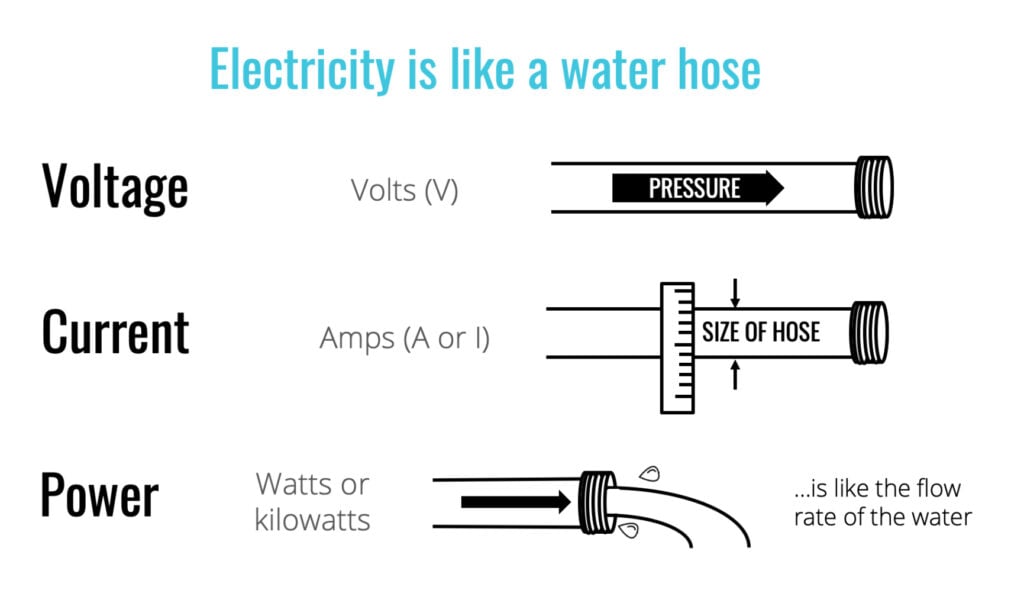
To find the power output of any EV charger, all you need to do is multiply its volts by its amps. This will tell you the watts an EV charger can deliver, and you can divide that number by 1,000 to find the kilowatts (kW).
For example, if an EV charger can carry 40 amps at 240 volts, it can output 9,600 watts (or 9.6kW) of power.
How Much Power Can an EV Accept?
At public charging stations, certain EV models can reach charging speeds up to 350 kilowatts. At any other type of charger, electric cars can only receive up to 19.2 kilowatts at 80 amps. To find the maximum amount of power your EV can receive, check the power rating of its on-board charger.
All electric cars have on-board chargers, which take the “alternating current” (AC) found in homes and converts it into “direct current” (DC), which your batteries need to charge. Basically, the on-board charger is its own separate charger inside your car, and it will determine the maximum charging speed of your EV.
For example, if your on-board charger has a power rating of 7.7kW, it will only be able to charge at a maximum of 7.7kW, even if you connect to an 11.5kW charger. If you connect that same electric car to a 5.6kW charger, it will charge at 5.6kW.
So, if you want your batteries to fill up as fast as possible, you should use an EV charger that can supply as much power as your on-board charger can handle – or more. You can find the power rating of your on-board charger in your electric car’s manual.
Read More: How to choose the right EV charger
How Many Amps Does an EV Charger Output?
Plug-in EV chargers can output up to 9.6kW at 40 amps, as long as you use the right 240-volt outlet. Hardwired chargers can supply up to 19.2kW at 80 amps. However, most electric cars on the market today have a maximum charging speed of 11.5kW at 48 amps.
Additionally, it’s worth considering whether your home’s electrical system can even handle a more powerful charger. Some homes may require upgrades to accommodate higher charging capacities.
- Hardwired
Hardwiring an EV charger means connecting it directly to your home’s electric system. While this requires an electrician to install the unit for you, it is safer and more reliable. In order to hardwire an EV charger, you will also need to have capacity available in your electric panel.
- Plug-In
If you already have a 240-volt NEMA outlet in your home, you might be able to plug an EV charger in without installing anything, but it won’t deliver as much power as a hardwired charger. The highest-rated NEMA outlets used for EV charging only carry up to 50 volts, but even then, you’ll only be able to charge your EV at 40 amps.
Which NEMA Outlet to Use for EV Charging
There are several different NEMA outlets you can use to charge an electric car, but some are faster than others. For the fastest charging speeds, you’ll want to connect to a NEMA 6-50 or a NEMA 14-50, both of which can supply up to 9.6kW at 40 amps.
Other outlets you can use for EV charging are the NEMA 14-30 and NEMA 10-30, but they only supply up to 5.6kW at 24 amps. On the other end of the spectrum, standard NEMA 5-15 outlets can only supply up to 1.4kW at 12 amps. These 120-volt outlets can take more than three days to fully charge an electric car.
Read More: Level 1 vs level 2 EV chargers
Since all wall-mounted chargers carry 240 volts, many of them will only advertise how many amps they can deliver. However, some chargers might list the amperage of the breaker, not the actual amps your EV will receive. The maximum charging speed you’ll actually get from any plug-in charger will be 9.6kW at 40 amps.
What Size Breaker Do You Need for an EV Charger?
Whether you hardwire an EV charger or install a 240-volt outlet, you’ll need to follow the 80% rule. According to the National Electric Code, EV chargers are classified as a “continuous load,” which means they can only use 80% of the capacity of the circuit they are attached to.
For example, if you hardwire an EV charger to a 60-amp breaker in your electric panel, it will only be able to output 48 amps. So, while you might see plug-in chargers that claim to deliver 50 amps, they will only be able to supply a total of 40 amps since that is the highest output for any NEMA outlet.
Read More: How long does it take to charge an electric car?
A standard 100-amp panel usually supports 20 circuit breakers, each at 120 volts. That means you’ll most likely have to use two circuits to support a level 2 EV charger. However, you might already have all your available circuits taken up by large appliances, like stoves and clothes dryers. If you don’t have available circuits, you might need to upgrade your electric panel, which can be expensive.
How Many Amps Can Your Home Handle?
Most residential homes built after 1970 have a 100-amp or 200-amp panel. This should leave enough room for a 60-amp EV charger, depending on how many other electric appliances and devices you have in your home. If your home has a 60-amp panel, you will probably need to upgrade before you can install an EV charger.
EV chargers pull a lot of power, so you’ll need a licensed electrician to come to your home to perform a load calculation. This calculation will determine the total electrical capacity of your home, how much electricity you regularly consume, and if you have enough power to safely install an EV charger.
If you need any help installing an EV charger in your home, HelloTech can send an electrician to your door to give you a free quote. We can provide an in-home quote in as little as 15-30 minutes, and our technicians can schedule your installation within a week or two of the estimate.


