Whether you just got a new electric car or you plan to purchase one soon, there are two main options to charge your car at home. Level 1 chargers are the cheapest and easiest way to charge your EV, but they can take days to fill up your batteries. Level 2 chargers are fast enough to fill your batteries overnight, but they usually need to be installed by a professional electrician. Here’s everything you need to know about the difference between level 1 vs level 2 EV charging in terms of power, speed, cost, and more.
Read More: EV charging guide
Level 1 vs Level 2 Charging: Power
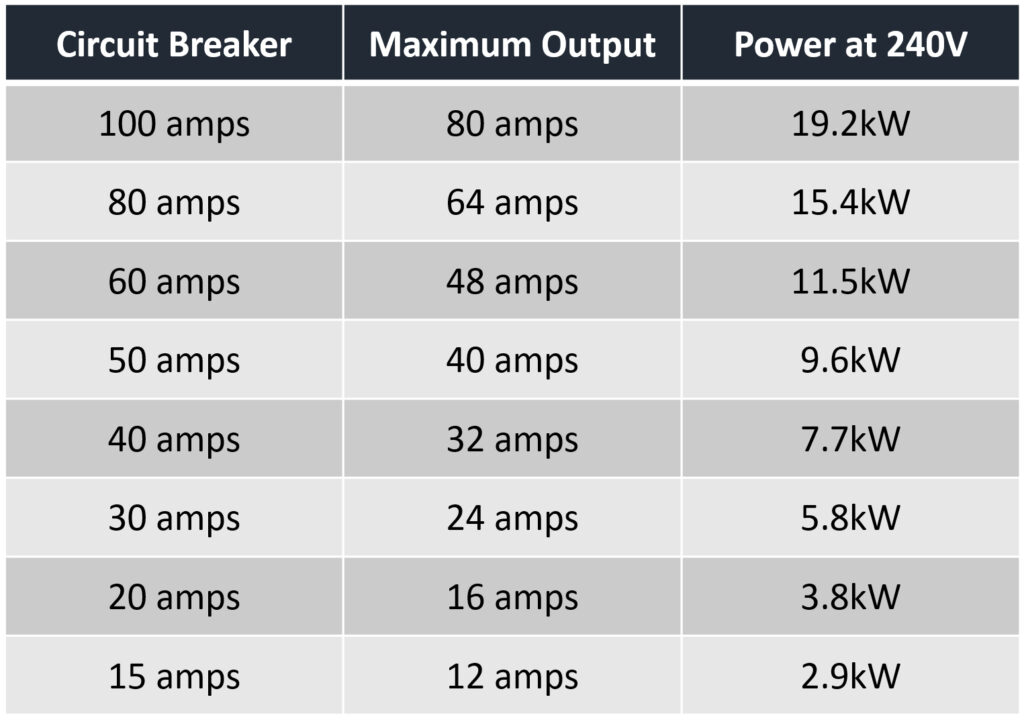
Level 1 chargers carry 120V (volts) at 10-20A (amps), which means they can deliver between 1.2–2.4kW (kilowatts) of power. On the other hand, level 2 chargers are capable of delivering 240V at 12-80A, or 2.9–19.2kW. That means level 2 chargers are a lot faster, but they also require more power, and you might need an electrician to install them.
Level 1
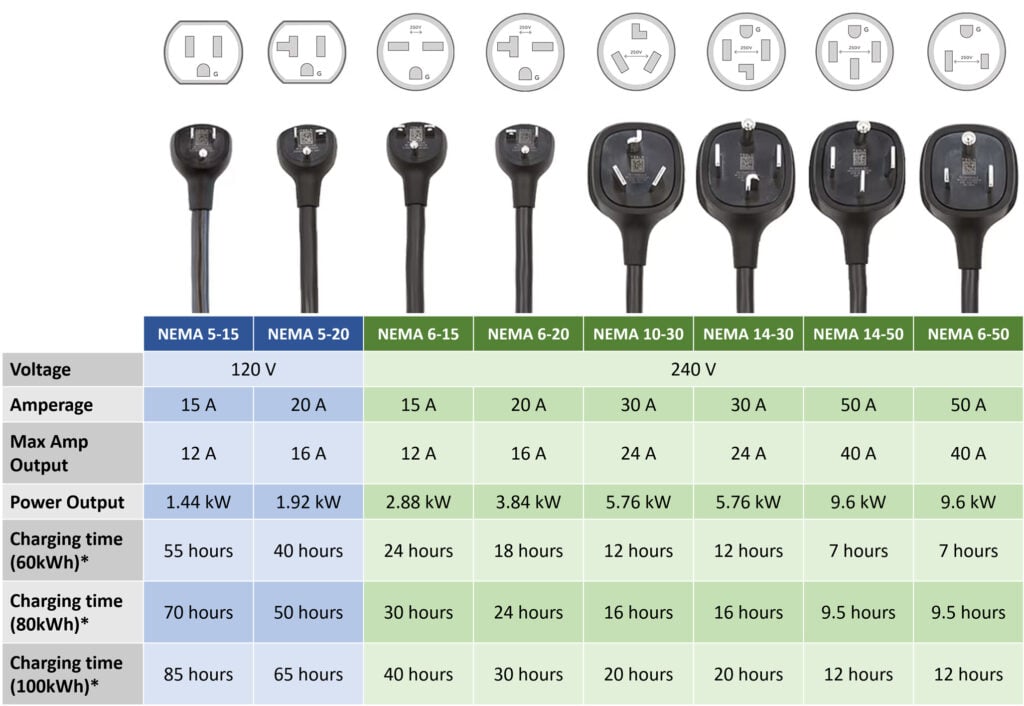
Using a level 1 charger is simple. All you have to do is plug your EV into an electrical outlet, but there are different types of outlets you can use. A regular household outlet is called a NEMA 5-15, and it carries 120V at 15A. However, your EV will only charge at 12A, so these outlets will only give you 1.44kW of power.
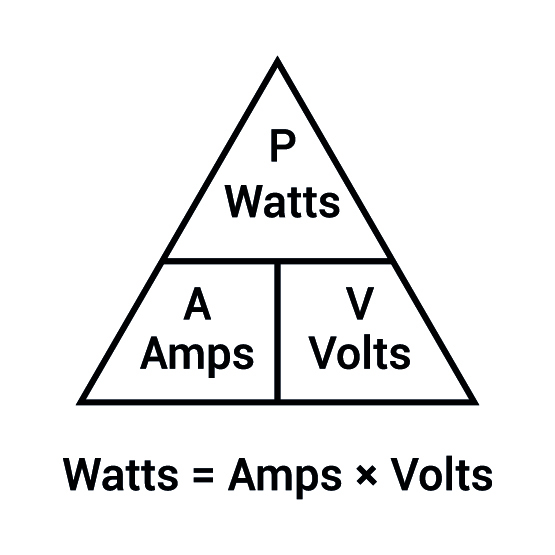
To find out how much power an outlet can deliver, all you have to do is multiply its voltage by its amperage.

Watt
A unit of electrical power. This number will tell you how much electricity your charger can deliver and how fast it will be able to fill up your batteries. The power output of EV chargers is measured in kilowatts (kW or 1,000 watts), and your electric car battery capacity will be measured in kilowatt-hours (kWh).
Volt
The electricity pressure in a wire. In the US, power is delivered to homes at two different voltages, 120V and 240V. Regular household appliances, like TVs, computers, lamps, and microwaves, only need 120V, while large appliances like stoves, clothes dryers, and air conditioners need 240V.
Amp
A unit of electrical current. You can think of amps like the load carried by a dump truck, and volts are like the speed of the truck. When charging your electric vehicle, you want the power source to have a as many volts and amps as possible, so it can deliver power as quickly as possible.
Level 2
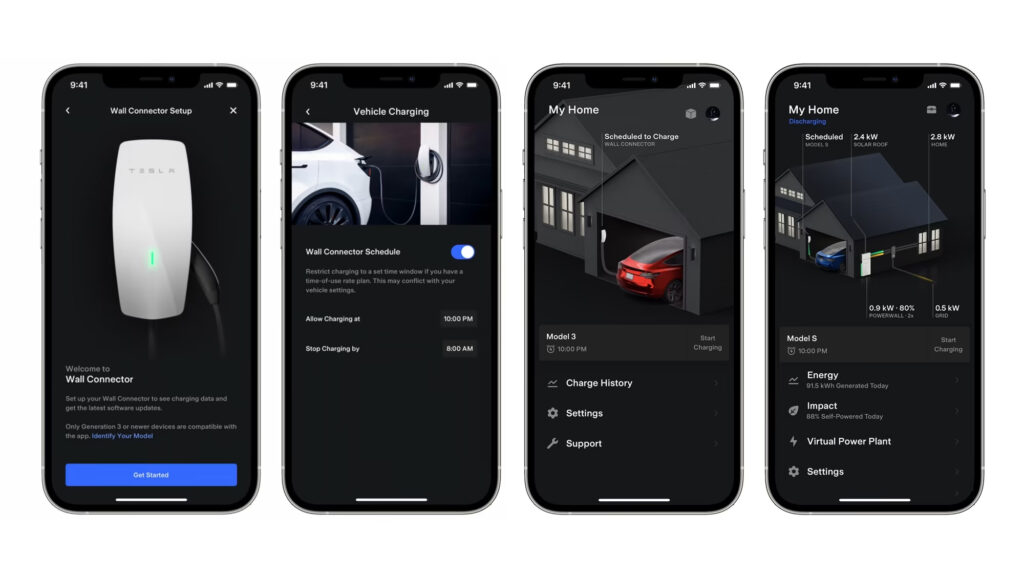
Level 2 chargers are faster, safer, and more convenient than level 1 chargers. If you install a wall connector in your home, you can fully charge your EV overnight. Level 2 wall chargers also come with smartphone apps that let you see how much energy you’re using and set charging schedules to help save money and energy.

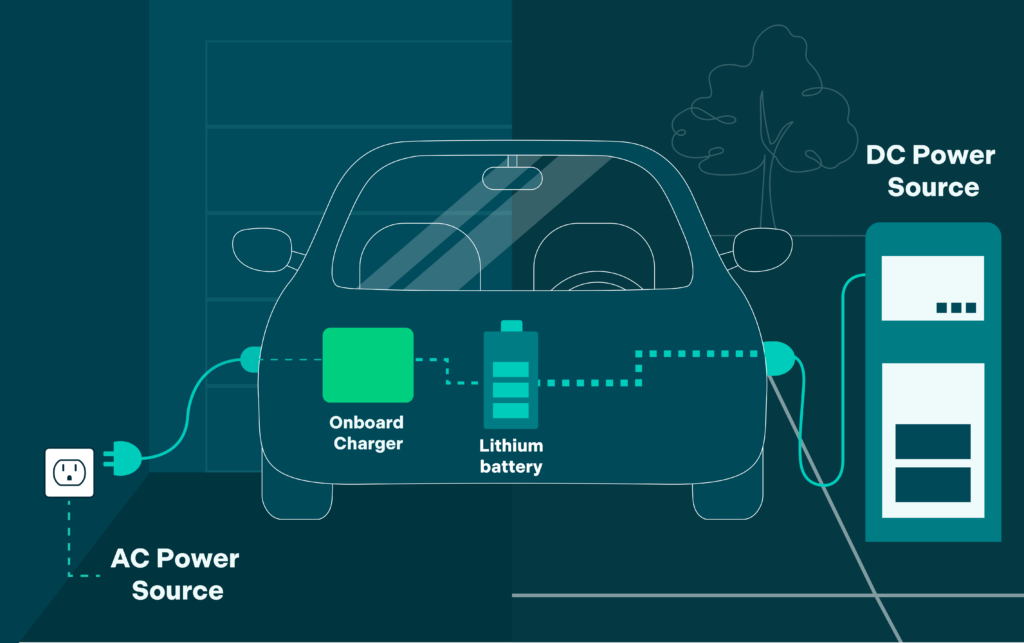
Before you install a level 2 charger in your home, make sure to check your EV’s onboard charger. All electric cars have a built-in onboard charger, which converts the alternating current (AC) found in your home into direct current (DC) to charge your batteries.
The power rating of onboard chargers can range anywhere from 3.7kW to 22kW, but you’ll typically find them between 7.7kW and 11.5kW. Once you know how much power your onboard charger can receive, choose an EV charger that can deliver as much power or more.
Hardwired vs Plug-In EV Chargers
There are three main options for installing a level 2 charger in your home. You can use an existing 240V outlet, as long as it can deliver enough power. You can also install a wall connector for a cleaner and safer charging station. Wall connectors can either be hardwired directly to your circuit breaker or plugged into a 240V outlet.
Hardwired EV Chargers
Hardwiring your EV charger means connecting it directly to a 240V circuit in your circuit breaker. While this requires an electrician to install the charger for you, it will be cleaner, safer, and more convenient in the long run. Without the extra wires hanging down, you have fewer issues due to faulty wiring.
With a wall charger, you can also track how much power you’re using and set up charging schedules with the companion smartphone app.
Plug-In EV Chargers
If you already have a 240V outlet in your garage, you might be able to charge your EV without installing anything. You can either plug your EV in using a charging cable , or you can mount a charger to the wall and plug that into the 240V outlet. However, not all 240V plugs deliver the same amount of power.
Whether you install a hardwired EV charger or a new 240V plug, you’ll need to follow the National Electrical Code “80% rule.” This means your charger can’t use more than 80% of the capacity of the circuit it is connected to. So, if you want to charge your electric car at 48 amps, you’ll need a 60-amp breaker.
Read More: How to choose the right EV charger
The electrical code now requires GFCI (ground fault circuit interrupter) breakers for all new 240v outlets. However, most EV wall chargers will already have GFCIs built-in, and having two GFCIs on the same circuit can cause them to trip each other.
Known as “nuisance tripping,” lots of new EV owners complain about plug-in chargers regularly blowing out their circuits and causing their power to go out. In fact, EV charger manufacturers warn against using a plug-in charger with a GFCI breaker, and they usually recommend installing a hardwired model instead.
Level 1 vs Level 2 Charging: Connectors
Currently, most electric cars in the US have an SAE J1772 connector built in, which will work with many level 2 wall chargers. However, most new EVs made after 2025 will use an NACS connector, which is the same connector Tesla uses for all its electric cars.
So, if you are planning to buy a new EV in the next few years, it’s a good idea to install a NACS wall charger. You can also install a universal wall charger that has both SAE J1772 and NACS connectors built-in, so you can charge any kind of EV without using adapters.
Read More: The best EV chargers to install in your home

For level 1 charging, you’ll need a special cable in order to plug your EV directly into an outlet. Each type of outlet will require a different type of connector, with the most common being the NEMA 5-15 and NEMA 5-20 for level 1 charging, or the NEMA 14-50 and NEMA 6-50 for level 2 charging.
Level 1 vs Level 2 Charging: Speed
It can take several days to fully charge an EV with a level 1 charger. On the other hand, you can easily fill up your electric car overnight with a level 2 charger. After just an hour, a level 2 charger can add 44 miles to a Tesla Model Y, but you’ll only get five miles of range per hour with a level 1 charger.
To calculate how long it will take to charge your EV, all you need to do is divide the battery capacity by the power input. With a level 2 charger, the power output will be determined by your onboard charger or the power output from your charger, whichever one is smaller.
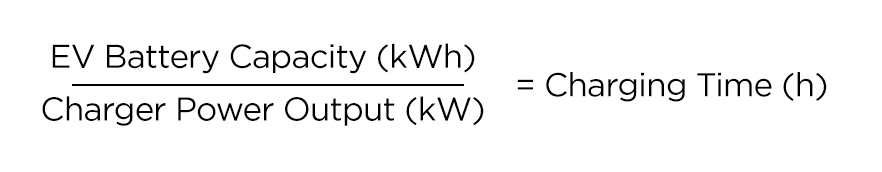
Read More: How long does it take to charge an electric car?
Level 1 vs Level 2 Charging: Cost
Purchasing a level 2 charger can cost $500-1,000 and up, just for the hardware itself. If you already have a 240V outlet, installing a charger can be cheap or even free. However, if you want to hardwire an EV charger or add a new 240V outlet, you should expect to pay at least $1,000 or more for the installation and permits.
Installing a level 2 charger in your home depends on how far your car is from a circuit breaker. The farther apart they are, the more it can cost. Also, if your home doesn’t have a powerful enough electrical system, it can cost more to upgrade it. However, most homes built after 1970 should work with EV chargers.
Once you have an EV charger in your home, then you’ll still need to pay for the electricity each time you fill up your batteries. Prices will vary based on where you live and how much your electric company charges per kilowatt-hour.
For example, the latest data from the US Energy Information Administration says that the average American spends around $0.16/kWh. So, if your electric car has a battery capacity of 100kWh, it should only cost $16 to fully charge.
Read More: How much does it cost to charge an EV?
It’s important to note that electricity costs can change dramatically from season to season and even hour to hour. To save money and energy, it’s recommended to charge your EV overnight, when demand is at its lowest. If your EV allows you to schedule your charging times,
If you need any help installing your EV charger, HelloTech can send an electrician to your door to give you a free quote. We can provide an in-home quote in as little as 15-30 minutes, and our technicians can schedule your installation within a week or two of the estimate.


