When you ask if a restaurant or cafe has WiFi, you want to know if you can connect to the internet. Does that mean that WiFi and internet are one and the same? Well, no; the two are actually completely different. So what is WiFi, what does it do, and what is the difference between WiFi and internet?
What Is WiFi?
Wi-Fi is a wireless networking technology that allows devices such as computers, smartphones, and smart home devices to connect to the internet or other devices without the use of wires. But that doesn’t mean Wi-Fi is the same as the internet. It is just one of the ways that you can access the internet.
What Does WiFi Stand For?
Wi-Fi is not an abbreviation of wireless fidelity. Phil Belanger, one of the founding members of the Wi-Fi Alliance, said that Wi-Fi doesn’t really mean anything at all.
“Wi-Fi doesn’t stand for anything,” Belanger wrote. “We needed something that was a little catchier than “IEEE 802.11b Direct Sequence.”
When it first started, the Wi-Fi Alliance hired Interbrand, a branding agency, to come up with the name and logo. However, the agency’s first tagline for WiFi was “The Standard for Wireless Fidelity,” so many people still get confused.
How Does WiFi Work?
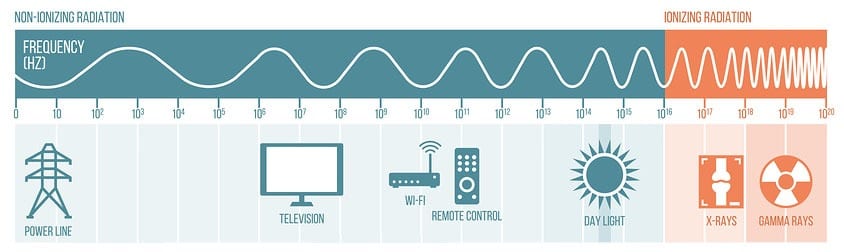
Wi-Fi uses radio waves to transmit data within a network of devices that are within a certain range. These radio frequency waves allow devices to connect to a router or to each other without the need for cables.
Remember how you used to access the internet? You had all kinds of cables and wires that connected your desktop computer to a modem over a landline. Now you don’t need these cables if you have Wi-Fi.
These days, your laptop has a WiFi adapter that connects to a router wirelessly. Your router transmits the actual internet connection that comes from your internet service provider (ISP), like Verizon or Comcast.
Take note, however, that you have to be within the signal range of the router to enjoy WiFi internet connectivity. Typically, the range of a WiFi network can reach up to 300 feet, but signal strength can be affected by walls, buildings, and other structures.
But range is just one of the things that affect your WiFi signal. If you’re experiencing slow WiFi, check out our post on the reasons your WiFi signal is poor and how you can fix it.
Wi-Fi also allows devices to communicate with each other. For example, a camera that has WiFi can connect to a laptop via a wireless network. Additionally, some printers that have WiFi can print your documents wirelessly, as long as your laptop is within its range. What this means is that WiFi can work without the internet, but it is typically used to connect to the internet.
What is the Difference Between WiFi and the Internet?
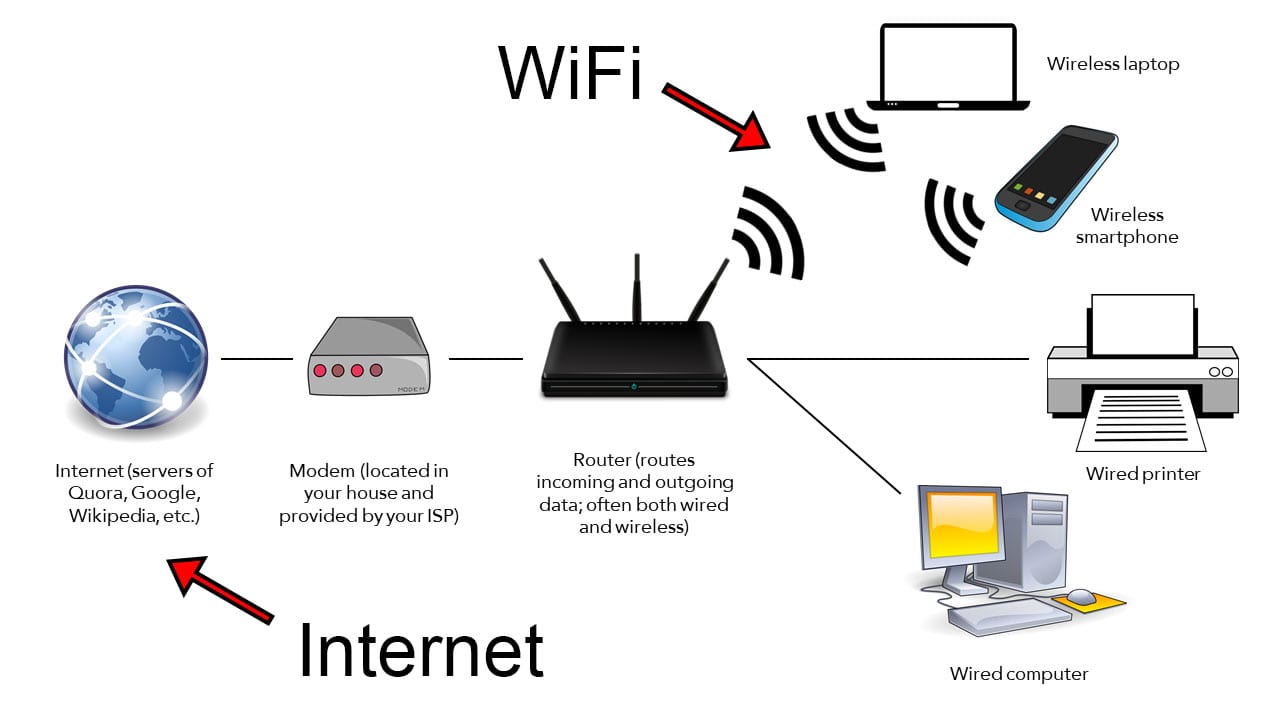
The internet is a public network consisting of millions of connected computers and data centers around the world. These computers transmit data via wireless connections, cables, telephone lines, and satellites.
Wi-Fi is just a signal that allows you to connect to the internet wirelessly.
To sum up, Wi-Fi is the trademarked term for a type of technology that lets your devices communicate with each other. Your smartphone, tablet, laptop, and other devices have WiFi adapters that let you connect to the internet. Which raises the following questions:
- If your device has WiFi, do you have internet automatically? No. You have to pay for internet, either from an internet service provider (ISP), or you can use mobile data from your phone company if you have a mobile hotspot.
- Can you access the internet without WiFi? Yes. You can still connect to the internet with the use of cables.
Additionally, Wi-Fi isn’t used solely for connecting to the internet. It’s also used for wireless communication between devices, such as between your laptop and a printer, an Amazon Echo and a smart thermostat, or a phone and a smart doorbell.


